Linked Tree Representation
- Implement binary heap with linked tree representation.
Exercise Suppose that a binary heap with $n$ nodes is implemented as a linked tree structure (not a ranked array). How can you get (find) the node (position) where the next leaf should be added in $\Omicron(\lg n)$ time?
Solution
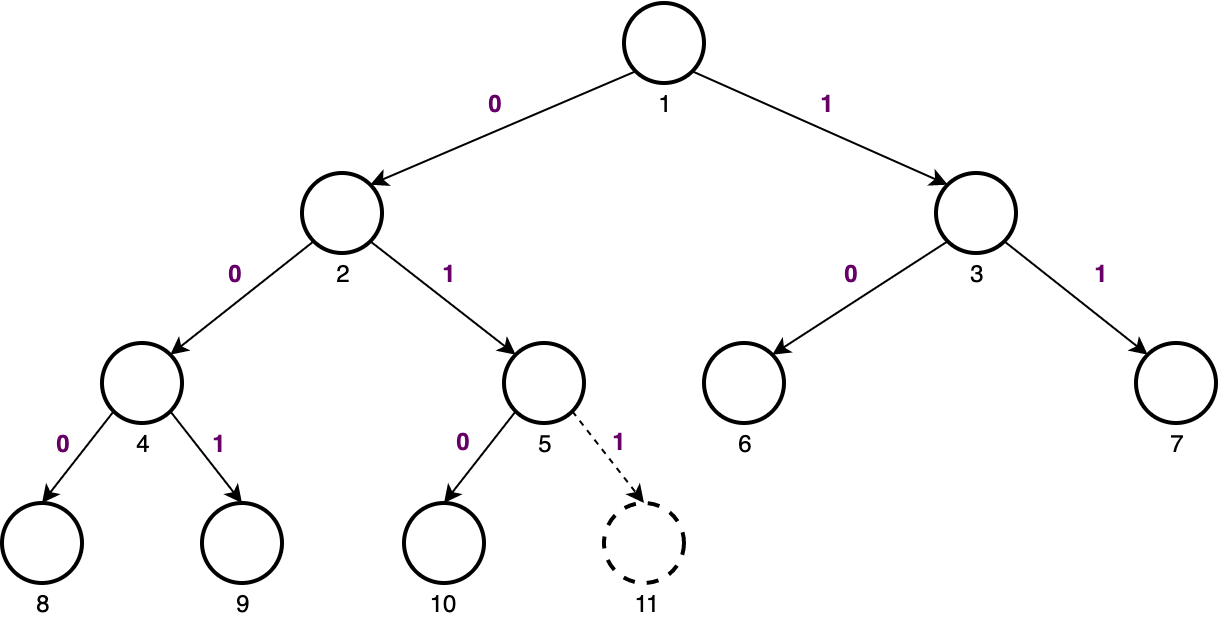
We can employ a clever trick based on binary numbers in conjunction with the ranked representation. Suppose we have already $10$ nodes in the binary heap, and we want to insert the $11^{\text{th}}$ node. We know the binary representation of $11$ is $1011$:
$$ 11_{10} = 1011_{2} $$
Now take the first digit (from left) of the binary representation to mean "start at the root" and for each remaining digit (from left to right) in the binary representation of the $k^{\text{th}}$ node, go left if the digit is $0$ and go right if it is $1$:
Exercise Here are a few unsolved (challenging) exercises:
-
You might want to add another operation to your PriorityQueue ADT to update (change) the priorities (values). Can you think of an approach to implement the
updateefficiently? -
You might want to take two priority queues and merge (combine) them. (Some references include a
meldoperation that does this). Can you think of an approach to implement this process efficiently?
Aside: Binary Heap is a clever implementation of PriorityQueue ADT. There are other variations of the heap data structure, namely the Binomial heap and Fibonacci heap. These implementations are beyond the scope of this course!